Cloud Firestore is a scalable database like Firebase Realtime Database, it keeps your data in sync across client apps through real time listeners and offers offline support for mobile and web so you can build responsive apps that work regardless of network latency or Internet connectivity.
The advantage of using Cloud Firestore is Expressive querying. You can use queries to retrieve individual, specific documents or to retrieve all the documents in a collection that match your query parameters. Your queries can include multiple, chained filters and combine filtering and sorting.
Here we store data in Documents. Documents are like Dictionaries a key value pair which support many different data types, from simple strings and numbers, to complex, nested objects.
These documents are stored in collections, which are containers for your documents that you can use to organize your data and build queries.
Querying in Cloud Firestore is expressive, efficient, and flexible. We can do query to retrieve data at the document level without needing to retrieve the entire collection, or any nested subcollections.
We can do pagination by adding sorting, filtering, and limits to queries. Adding realtime listeners to your app notifies you with a data snapshot whenever the data your client apps are listening to changes, retrieving only the new changes.
Next open Firebase Console -> Database -> Cloud Firestore, next pop up will come with two options, select start in test mode then enable.
Add the following dependencies to podfile:
Save the file, Run 'pod install' and open the created .xcworkspace file.
Next, We need to initialize Firebase.
Open Xcode project.
First import the Firebase SDK in AppDelegate.swift file:
Then, in the application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: method, initialize the FirebaseApp object:
Add the following code in viewDidLoad() method:
By the way, here we are storing friends name and his/her profession. Above reference is the path where we are going to store our data as a Document.
Next add the code for saving data. Add the following code in save button action method:
Run and enter the data in text fields, then tap save button. We will see message as 'Data has been saved'.
Next open Firebase console -> Database -> Cloud Storage:
Fetching is very simple, we need to get the data from same docRef.
Before that add fetch button to the view and give action outlet.
Add the following code inside fetch button action method:
Run and tap Fetch button, we will see the data at the top like follow:
Next add the viewWillAppear() method as following:
Above listener will keep on calling every time the data changes. So we need to remove the observer on viewWillDisappear. So that we can avoid memory problems.
Add the following method:
Run the project, we can see the title without tapping fetch button. That's good.
Next step is update data in real time. Now add some text in text field then tap save button.
On saving only we can see the title changes in real time without fetch action.
Download sample project with examples :
The advantage of using Cloud Firestore is Expressive querying. You can use queries to retrieve individual, specific documents or to retrieve all the documents in a collection that match your query parameters. Your queries can include multiple, chained filters and combine filtering and sorting.
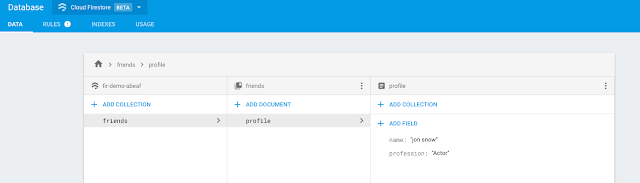
Data Structure:
Cloud Storage data structure will be like following image:Here we store data in Documents. Documents are like Dictionaries a key value pair which support many different data types, from simple strings and numbers, to complex, nested objects.
These documents are stored in collections, which are containers for your documents that you can use to organize your data and build queries.
Querying in Cloud Firestore is expressive, efficient, and flexible. We can do query to retrieve data at the document level without needing to retrieve the entire collection, or any nested subcollections.
We can do pagination by adding sorting, filtering, and limits to queries. Adding realtime listeners to your app notifies you with a data snapshot whenever the data your client apps are listening to changes, retrieving only the new changes.
Getting Started:
First create sample project in Xcode and add one UILabel, two UITextField's and one UIButton and give outlets. Build and Run that should look like as below:Next open Firebase Console -> Database -> Cloud Firestore, next pop up will come with two options, select start in test mode then enable.
Set up Firebase Cloud Firestore To iOS Project :
Next getting into Sample Project,First Integrate your project with Firebase.Add the following dependencies to podfile:
pod 'Firebase/Core' pod 'Firebase/Firestore'
Save the file, Run 'pod install' and open the created .xcworkspace file.
Next, We need to initialize Firebase.
Open Xcode project.
First import the Firebase SDK in AppDelegate.swift file:
import Firebase
Then, in the application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: method, initialize the FirebaseApp object:
// Use Firebase library to configure APIs FirebaseApp.configure()
Saving/Adding data to Cloud Firestore:
Open ViewController.swift, add the docRef property.var docRef : DocumentReference!
Add the following code in viewDidLoad() method:
docRef = Firestore.firestore().document("friends/profile")
By the way, here we are storing friends name and his/her profession. Above reference is the path where we are going to store our data as a Document.
Next add the code for saving data. Add the following code in save button action method:
@IBAction func saveButtonTapped(_ sender: UIButton) {
guard let name = nameField.text, !name.isEmpty else { return }
guard let profession = professionField.text, !profession.isEmpty else { return }
let dataToSave : [String: Any] = ["name": name, "profession": profession]
docRef.setData(dataToSave) { (error) in
if let error = error {
print("Oh no! Some error \(error.localizedDescription)")
}else {
print("Data has been saved")
}
}
}
Run and enter the data in text fields, then tap save button. We will see message as 'Data has been saved'.
Next open Firebase console -> Database -> Cloud Storage:
Fetching/Getting data From Cloud Firestore:
Fetching is very simple, we need to get the data from same docRef.
Before that add fetch button to the view and give action outlet.
Add the following code inside fetch button action method:
@IBAction func fetchButtonTapped(_ sender: Any) {
docRef.getDocument { (docSnapshot, error) in
guard let docSnapshot = docSnapshot, docSnapshot.exists else { return }
let data = docSnapshot.data()
let name = data["name"] as? String ?? ""
let profession = data["profession"] as? String ?? ""
self.titleLabel.text = "\(name) is a \(profession)"
}
}
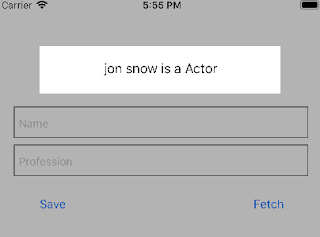
Run and tap Fetch button, we will see the data at the top like follow:
Listening for RealTime in Cloud Firestore:
First add the following listener property.var dataListener : FIRListenerRegistration!
Next add the viewWillAppear() method as following:
override func viewWillAppear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewWillAppear(animated)
dataListener = docRef.addSnapshotListener { (docSnapshot, error) in
guard let docSnapshot = docSnapshot, docSnapshot.exists else { return }
let data = docSnapshot.data()
let name = data["name"] as? String ?? ""
let profession = data["profession"] as? String ?? ""
self.titleLabel.text = "\(name) is a \(profession)"
}
}
Above listener will keep on calling every time the data changes. So we need to remove the observer on viewWillDisappear. So that we can avoid memory problems.
Add the following method:
override func viewWillDisappear(_ animated: Bool) {
super.viewWillDisappear(animated)
dataListener.remove()
}
Run the project, we can see the title without tapping fetch button. That's good.
Next step is update data in real time. Now add some text in text field then tap save button.
On saving only we can see the title changes in real time without fetch action.
Conclusion:
Cloud Firestore offers robust access management,Expressive querying and authentication. Secure data by using authentication and rules.Download sample project with examples :



















FIRListenerRegistration is changed into ListenerRegistration.
ReplyDelete